Concentration measurement in lyes
The concentration measurement in lyes is a fundamental step in numerous chemical processes and industrial applications. It determines the exact concentration of a lye in a solution. This is crucial for understanding and utilizing the chemical properties and reaction behavior of the lye.
Among the most common lyes used in chemistry are: Sodium hydroxide (NaOH), also known as caustic soda, Potassium hydroxide (KOH), calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)₂), ammonium hydroxide (NH₄OH), magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)₂) and Lithium hydroxide (LiOH).
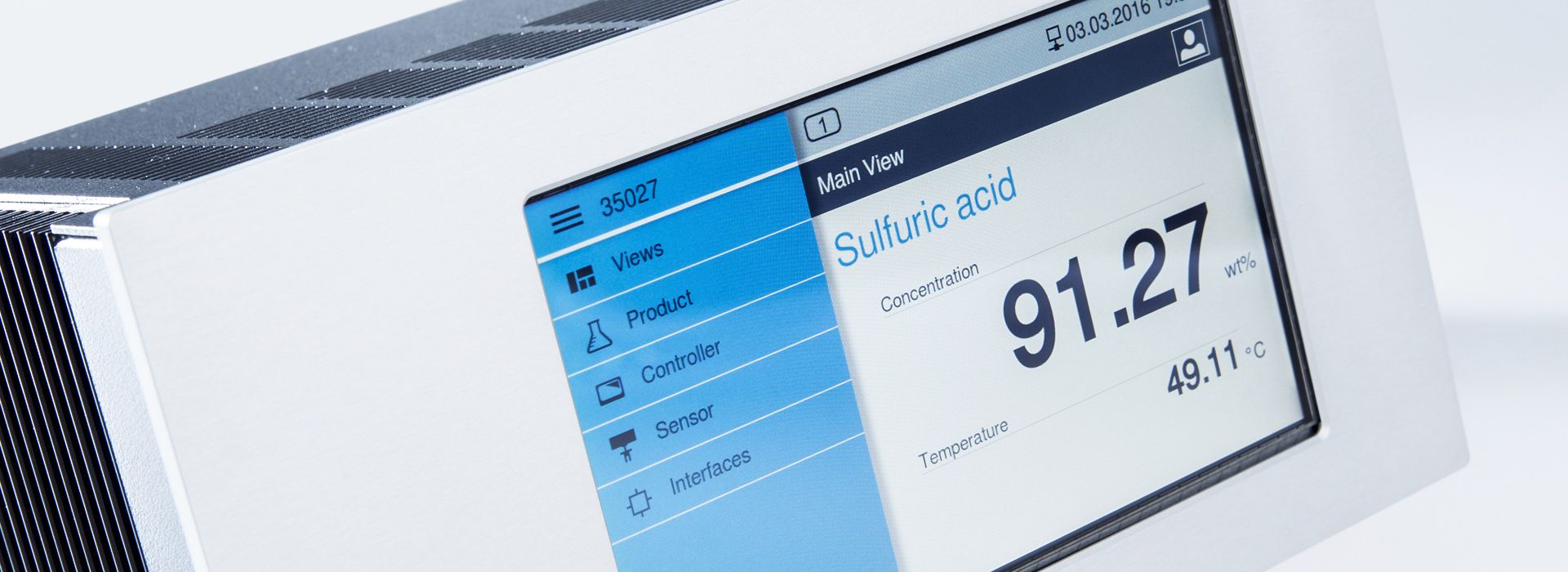
Concentration measurements with LiquiSonic® measuring devices
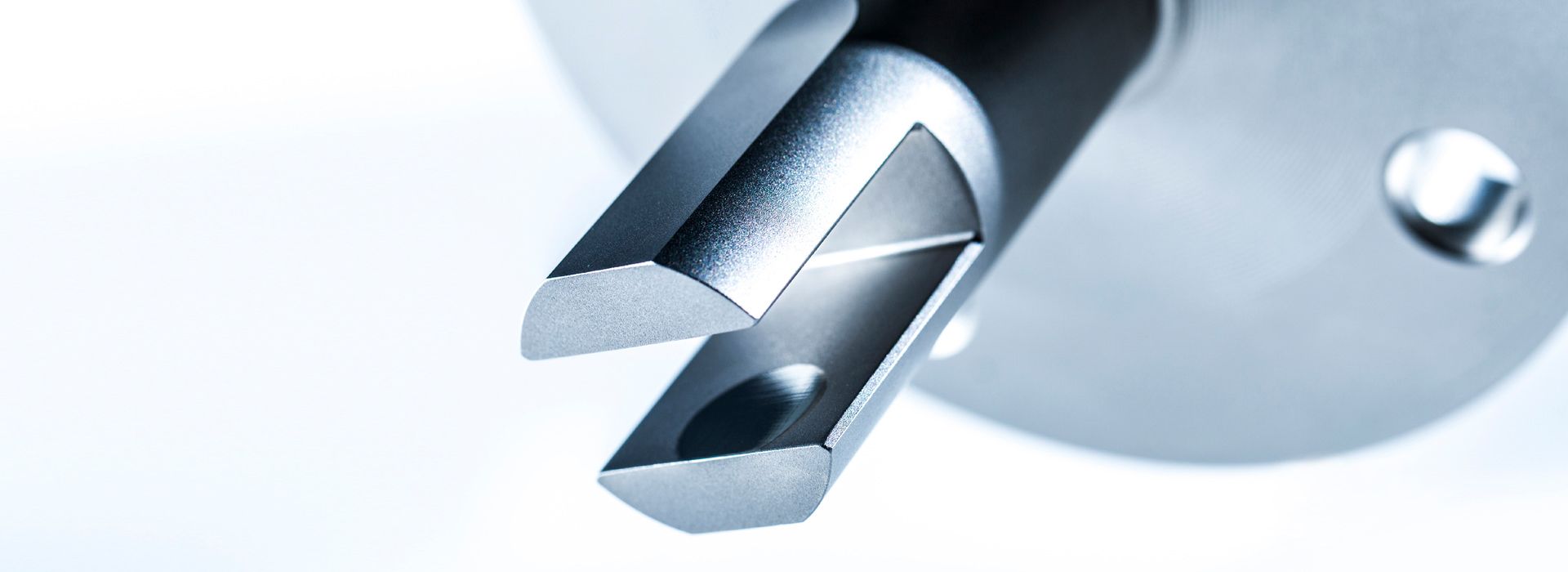
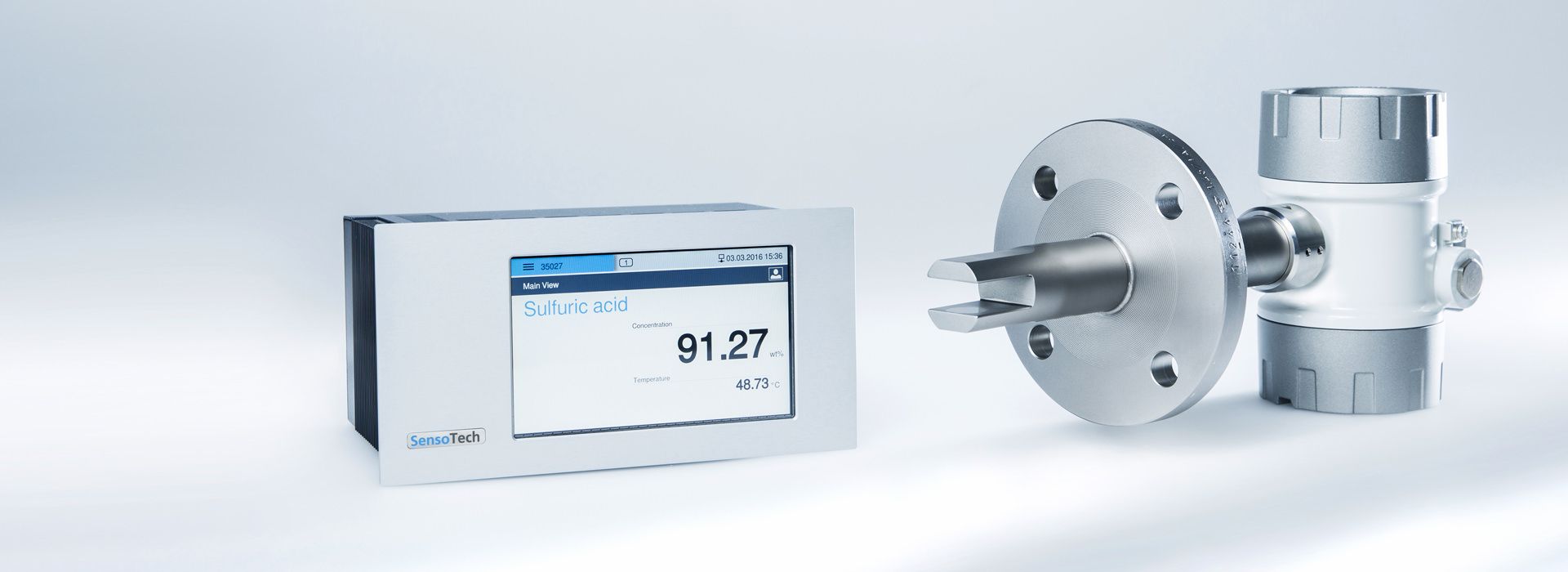
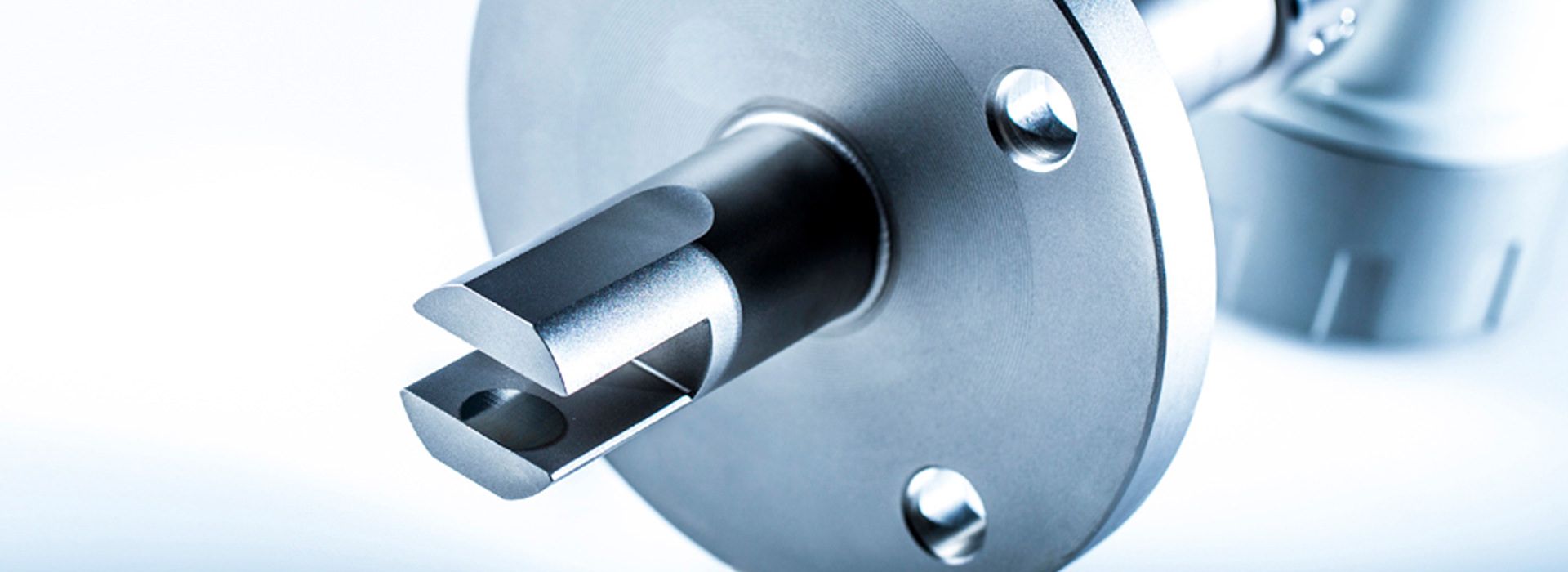
The LiquiSonic® measurement systems enable inline concentration measurements of lyes. The measurement technology can analyze the components of mixtures and provide information on concentration or density in real-time. The sensors are based on the principle of ultrasonic speed measurement. They are thus almost maintenance-free and can reliably provide measurements even under demanding conditions.
Installation of LiquiSonic® measurement systems
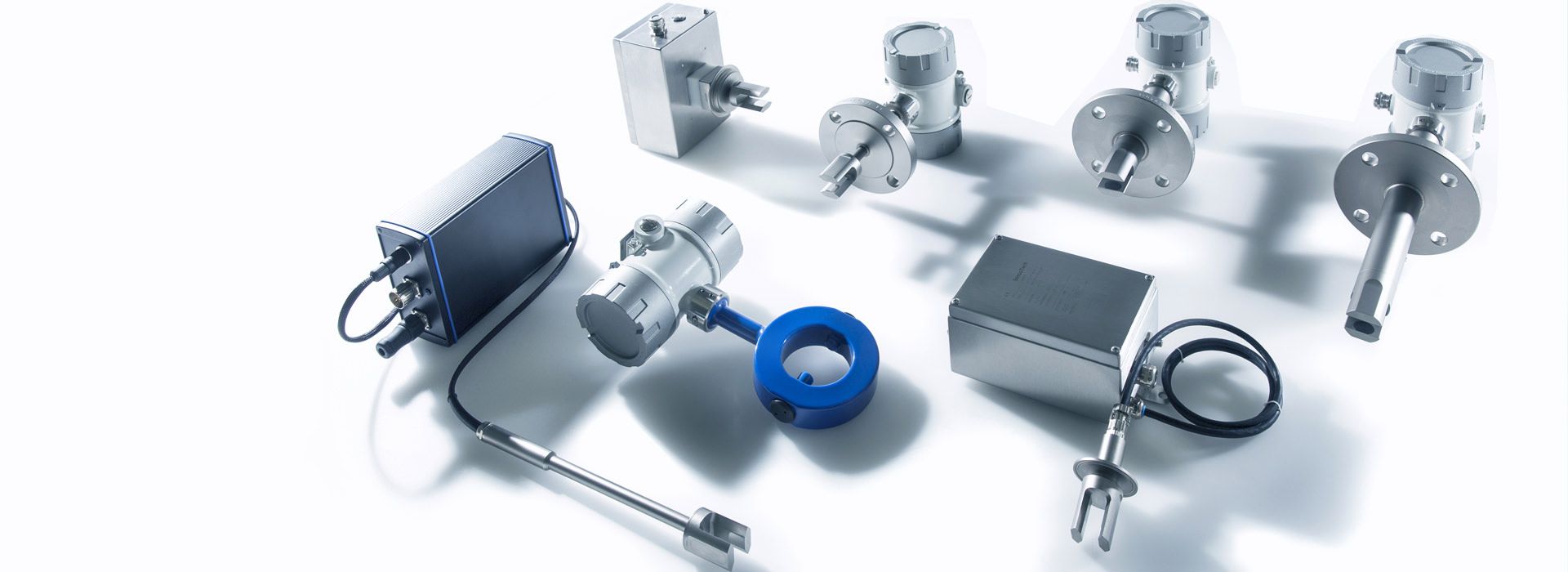
The LiquiSonic® sensors can be installed directly into the user's system, for example in pipelines, without a bypass. There are also various versions tailored to specific applications with distinct features.
Applications of concentration measurements
Concentration measurement is one of the essential methods for analyzing the quality and safety-relevant characteristics of products and substances. It thus plays a crucial role in several industries.
A practical example of the application of concentration measurement is found in the pharmaceutical industry: Here, the precise determination of the active ingredient concentration in medications is essential to ensure their efficacy and safety. This highlights the importance of precise concentration measurement methods in quality assurance.
Concentration detection is used in the following areas:
- Chemical production (To monitor the composition of mixtures)
- Pharmaceutical industry (e.g., for the production of medicines)
- Food production (To control the quality of food)
- Metallurgy (To check the quality of metal ores)
In addition, concentration measurement is also commonly used in other areas within industry and science.
What is a lye?
A lye, often referred to as an alkaline solution, is an aqueous solution that contains hydroxide ions (OH⁻). Lyes are formed by dissolving a base in water and are characterized by their ability to neutralize acids in a neutralization reaction. They often have a soapy feel, can dissolve organic substances such as fats and oils, and change color indicators (such as phenolphthalein) in a manner typical for bases.
How is the concentration of a lye determined?
The concentration of lye can be determined in various ways. Some common methods are:
- Sound velocity measurementThe measurement of the speed of sound in a solution is used to determine the concentration of a lye. This method is based on the fact that the speed of sound in a liquid depends on the density and elastic properties of the solution, which are in turn influenced by the concentration of the dissolved substances. When measuring the speed of sound, a sound pulse is sent through the solution, and the time it takes to travel a known distance is measured. From thisTime and the distance can be used to calculate the speed of sound.
- TitrationOne of the most common methods for determining the concentration of a base is acid-base titration. The base is reacted with an acid of known concentration until a neutralization point is reached. The consumption of the acid can be used to calculate the concentration of the base. Indicators or pH measurements are used to determine the endpoint of the titration. Titration is time-consuming, labor-intensive, and can be inaccurate with dilute solutions or in the presence of interfering impurities.
- pH measurementThe concentration of strong bases can also be determined by direct measurement of the pH value. Since the pH value is a measure of the hydrogen ion concentration and strong bases dissociate completely, the concentration of the base can be calculated from the pH value. For weak bases, however, this relationship is not direct and requires more complex calculations.
- Conductivity measurementThe electrical conductivity of a solution depends on the concentration of dissolved ions. Therefore, conductivity measurement can be used to determine the concentration of a base. This method is particularly useful for solutions that are highly ionic. However, it is also sensitive to the presence of various ions, which can lead to inaccuracies, and is complicated in calibration.
- Spectroscopic methodsFor bases that contain specific absorbing or emitting species, spectroscopic techniques such as UV-Vis spectroscopy can be used to determine the concentration. The intensity of absorption or emission is related to the concentration of the base. These methods require specific absorbing or emitting species in the solution and are unsuitable if such properties are absent or disturbed by other substances.
Applications of concentration measurements of bases
Concentration measurements of bases are relevant in various fields and applications. These include, among others: Soap and detergent manufacturing, neutralization reactions, pH regulation, chemical synthesis, extraction processes, biomass decomposition, wastewater treatment & corrosion protection.